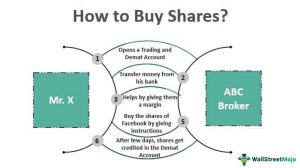
Unraveling the Mystery of Falling Stock Prices
Feeling like watching your financial dreams come crashing down with the stocks that keep hitting the ground? Let’s embark on our mission to discern the reasons for which stock prices tend to precipitate by using real data, real historical examples, and real no-nonsense analysis. Grab your parachute and follow me.
The Economy
First and foremost, the economy plays a huge role in the performance of the stocks. If an economy were to enter a recession, stock prices would decrease on the whole. This was the case with the recession of 2008, when the S&P 500 morphed into the S&P 300 , losing nearly half of its value. Economic indicators such as GDP , employment numbers, and consumer confidence are extremely indicative of economic health and can easily predict when future stock prices are going to fall. For instance, an increase in the unemployment rate will result in less spending on behalf of consumers, a situation which will drive down corporate profits and stock prices.
Company Performance
Naturally, the better a company performs, the higher its stock prices are likely to get. This is because earnings determine stock prices, which means that if a company releases a quarterly earnings report which is lower than the market anticipated, you can expect prices to drop rapidly. For instance, if Apple were to report a quarterly revenue which is under what analysts had expected, its stock price would recede. This is because shares are essentially claim checks on the company’s earnings and assets, meaning the higher earnings and assets of a company, the higher their worth will be. It is also important to focus on revenue growth, profit margins and what sort of guidance the company will provide for future performance.
Market Sentiment
Sometimes, stock prices fall because investors get skittish. This can be the case not only for their specific company they are conmissive of but likely of the entire stock market or of a specific stock market. For instance, in 2000, the market was suffering from irrational exuberance with regard to the dotcom boom of 1999. This boom was followed by a 20% decrease of the market once the enthusiasm pretty much died off.
External Shocks
Every once in a while, something will happen. A hurricane, or a technological breakthrough, or a nuclear war, or a comet will hit. In 2020, COVID struck. The stock market nosedived.
Interest Rates and Monetary Policy
On occasion, the Federal Reserve will decide to mastermic interest rates. This can influence the performance of the stock market. For instance, an increase in the interest rates will raise stock prices because corporations will be forced into borrowing at high rates. However, this is not always applicable and one should not expect or disregard such a notion without conducting further, more comprehensive research.
Analysis of Specific Industry Trends
Every decade or two, fossil fuels stock prices are likely to decrease by a lot. Which is why?
In conclusion, if you really wish to be successful on the stock market, you must understand what drives money. Odds are, money is driven by forces and you must comprehend these forces. Dropping prices is not the end of the world – quite the opposite, it is a beginning of a lot of learning. Just remember, reacting to money is not all there is. You must always seek to know how the wind blows.
Investor Perception and Stock Value
When analyzing the reasons why the stock price falls, it is crucial to consider how investor perceptions dictate market value. In many cases, investors’ reactions to news, economic data, and company performance drive stock prices to a greater extent than the actual financials.
Negative News
Negative news, concerning the economy, a particular sector, or a company, are the easiest way to make investors change their perception. For example, when the tech giant Facebook is caught in a data misuse scandal, investors might fear regulatory backlash and selling of shares, which decreases FB price significantly. Essentially, this is a reaction from stock owners who do want to lose their money.
Psychological Factors of Trading
Not all trading decisions make perfect sense, as these are human beings that sometimes suffer from psychological bias. When the market starts feeling fear and uncertainty, it may easily overreact. At the beginning of 2020, when it became clear that the coronavirus is going to be a global pandemic, S&P 500 dropped more than 30% in a few weeks.
The Impact of Analyst Ratings and Forecasts
Ratings and forecasts of analysts greatly impact the way stocks are perceived. It is possible that a stock of a company might fall if a major analyst downgrades it, even if there was no other reason for the stock’s decline, and the company’s actual financial health did not change. Similarly, upgrades temporarily make prices go up.
Market Trends Identified with the Help of Technical Analysis
Those who follow technical analysis, which is the study of stocks’ past price movements to identify patterns and signals, note it is also a reason for stock prices to fall. When it is clear that its price fell to such an extent it reaches a “bearish” pattern, such as breaking below its 200-day moving average or forming “death crosses” , it is expected to continue declining, which prompts technical traders sell their stock now.
It is possible, and, in many cases, quite logical, to try to predict the future stock price with a better understanding of investor psychology and market sentiment rather than studying such economic indicators as profits of a particular company.

Supply and Demand Dynamics
The basic principle of supply and demand undoubtedly affects the stock price. This economic model helps explain why the price for stocks changes according to their availability for sale and the investors’ desire to buy.
Fluctuations in Share Availability
The change in the number of shares available influences the stock price. For example, if a company issues more shares on the market or its large investors decide to sell the corporation’s holdings, the supply increases. Therefore, the equity price decreases. Thus, if this week, Tesla declares its intention to hold the secondary offering of shares to get capital, the stock price of the company may reduce at once.
Change in Investor Demand
Demand for stocks changes due to various indicators, including economic factors, development of the sector in general, and world events. For example, in the late 1990s, due to the development of technologies, the demand for stocks in this sector was enormous. Gradually, with the growth of the Nasdaq, investor interest in technology companies became overly significant, which eventually led to a market crash known as the dot-com bubble .
Influence of Large Institutional Investors
If a large pension or mutual fund decides to alter its portfolio and reduce its stake in the pharmaceutical sector, its sales could lead to the stock price downfall of the pharmaceutical companies in general.
Market Speculation
One of the reasons a price can change is the sale or purchase of stocks due to expectations regarding possible changes in prices in the future. For example, if a trader assumes that the value of a particular share is too high and it may fall soon, many market players will want to earn money through short sales. Iterate, this activity will lead to the stock price falls. In this way, all of the above reasons can both increase and decrease the stocks’ market prices.
Fundamental Dynamics Steering Our Stock Value
This discussion aims to provide an understanding of the basic dynamics that may be causing the value of your stock to decrease. I will examine key financial indicators and industry-related analyses. If a major company finds a material drop in its profit, for example, due to increasing costs of operation, its stock is likely to decrease in value . Thus, it is imperative to check regularly the income statements and comparable figures to understand the situation regarding your securities. Moreover, if other companies within the industry are losing value because their production or other costs are increasing, there is a high probability that your stock will decrease, as well.
In this case, it is possible to consider information related to the pharmaceutical industry. If new regulations in the U.S., for example, increases manufacturers expenses as companies are required to comply with them, stocks of these firms will drop. Since the industry, in general, is negatively impacted, it is likely that, regardless of how well these firms are managed, their value will not grow. Furthermore, it is possible to add that the general situation in the U.S. also affects the value. Despite that we know the circumstances are indirectly contributing to the decrease in stocks by increasing the expenses of companies, it is necessary to monitor these dynamics. For this, it may be useful to look at the such overall economic indicators, including GDP growth rate, unemployment rate, and consumer confidence changes. Finally, the war between the U.S. and China may be mentioned as an important event affecting the value of all stocks, although it would only concern some of them.
Fundamental Drivers of Stock Performance
In order to understand why a stock may keep going down, it is essential to analyze some of the most critical drivers that affect stock performance. This includes corporate earnings, competition in the market, as well as the overall economic environment. Throughout the broader stock analysis, these factors are explored in detail with the support of data and related examples.
Earnings and Corporate Profitability
First and foremost, the fundamental data that impacts a firm’s stock prices are corporate earnings. A growing company’s ability to earn a profit consistently is the primary driver of its stock value. As such, for instance, if Microsoft is constantly growing as a tech giant, launches successful products, and sees its earnings grow consistently from year to year, its stock price will increase . In contrast, if the company’s products are perceived as not being competitive and its earnings stagnate or decrease, its stock price would also significantly decrease . As such, the key priority lies in analyzing the income statement and the factors that impact the profitability of a company.

Market Competition
The second most critical factor that drives stocks down is based on the competition between companies. If a company’s competitive position within a particular industry dwindles due to active competition, its value in the stock market will decrease. For instance, BlackBerry’s stock price is now valued at $6.01 having lost most of its phone market share to Apple Inc. and Samsung .
Economic Environment
Finally, economic conditions that affect the stock market value include interest rate policy changes, inflation rates, as well as overall economic performance. For example, companies incur additional costs when inflation rates are high. Consequently, their profit margins are reduced, and their prices in the market decrease.
Technology Innovations and Trends
Last but not least, technology and its applied innovations may have an impact on whether a product is outdated by a new version of a product or replaced by a different form of technology or a related product. For instance, the rise of digital cameras has destroyed Kodak .
Valuation Multiples and Investor Expectations
The question about why a stock is decreasing is not possible to answer without understanding how valuation multiples and investor expectations drive stock prices. In this part, the following metrics will be considered to evaluate stock values and what happens when the fundamental assumptions that underlie the stocks change.
Role of P/E Ratios in Stock Valuation
The price-to-earnings is one of the most valid and critical ways that investors used to see whether the stock is undervalued or overvalued with respect to stock history or the general industry norms . For example, if the average P/E for the tech sector is 25 and Google has a 40 P/E largely because investors are so optimistic about the profit growth, the stock may be still overvalued. In contrast, if Google’s profit drops due to a certain reason, the price of the stock may immediately drop to coincide with the normal valuation multiple in technology – for instance, P/E of 20 .
Shift of the Market Sentiment
Another aspect is how people feel about future performance. For instance, investors believe that interest rates may fell, and thus slow economic growth. In such a case, they will decrease the value of stocks. Sometimes, stock prices are adjusted as investors anticipate a change in the economic circumstances even before there is any real change in the economic situation.
Shifts in the Investor’s Risk Appetites
Global changes or changes in the specific sector of the economy may affect investors’ risk appetite. In case the world gets less risky, there may occur a powerful effect. For instance, during a local political crisis or recession, the investors may shift from risky assets and decide to buy government bonds or gold, which results in decreasing the stock markets. The 2008 crisis is an example of how the world became very risky which led to the literal overnight revaluation of almost all the assets as risk becomes unacceptable. Taking into consideration the valuation multiples and comparing them to investors’ expectations and market sentiments allows predicting stock price movements. This knowledge is vital for implementing sound order execution strategies that will be considered in the following sections.
Evaluating When to Sell or Hold
Deciding whether to sell or hold a stock is an important consideration, particularly when faced with a series of declines. This essay will help the investor understand the relevant indicators and strategic considerations that help one arrive at the decision.
Assessing the performance
Before one sells a stock, the individual should look at both the short-term and long-term performance. For example, if the investor has stock in Netflix and the asset shows a dip that can be attributed to a temporary deviation from expectations that the quarterly earnings reports present, you may want to hold. However, if the performance seems to fade throughout historical performance, it would be a good idea to sell. Assessing how well the price is likely to grow considering the expected future performance of Netflix is vital in making a decision.
Assess the market and economic conditions
The performance of the stock you are considering to sell should be analyzed from the prism of the overall market and the economic conditions of the world. For example, a significant market performance that can be attributed to economic recessions or geopolitical challenges would not warrant the sale of the stock under consideration. Most of the measures of the performance of the stock would bounce back.
Reassess the fundamentals
Go back to the fundamentals of the stocks and understand the value of the stock in the context of the factors that motivated the investor to buy. Do the fundamentals remain strong? If they do, the investor should continue holding the stock. For example, if the competitive advantage offered by the management remains the same and the financial health of the company is still stable, the investor may want to hold rather than sell. Otherwise, the investor would consider selling.
The role of diversification and portfolio balance
Even if the investor believes the stock that is under consideration provides a substantial profit in the long-term, the individual should consider selling it if holding it would disrupt their portfolio balance. Having the mix that understands risk tolerance is an important consideration in making the decision. Portfolio management strategies often require regular selling. Based on these considerations, the holding considerations of any stocks can be made.